Didjay F. Bruggeman, Remko J. Detz, Simon Mathew & Joost N. H. Reek
Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2024
DOI: 10.1007/s43630-024-00534-5
Abstract
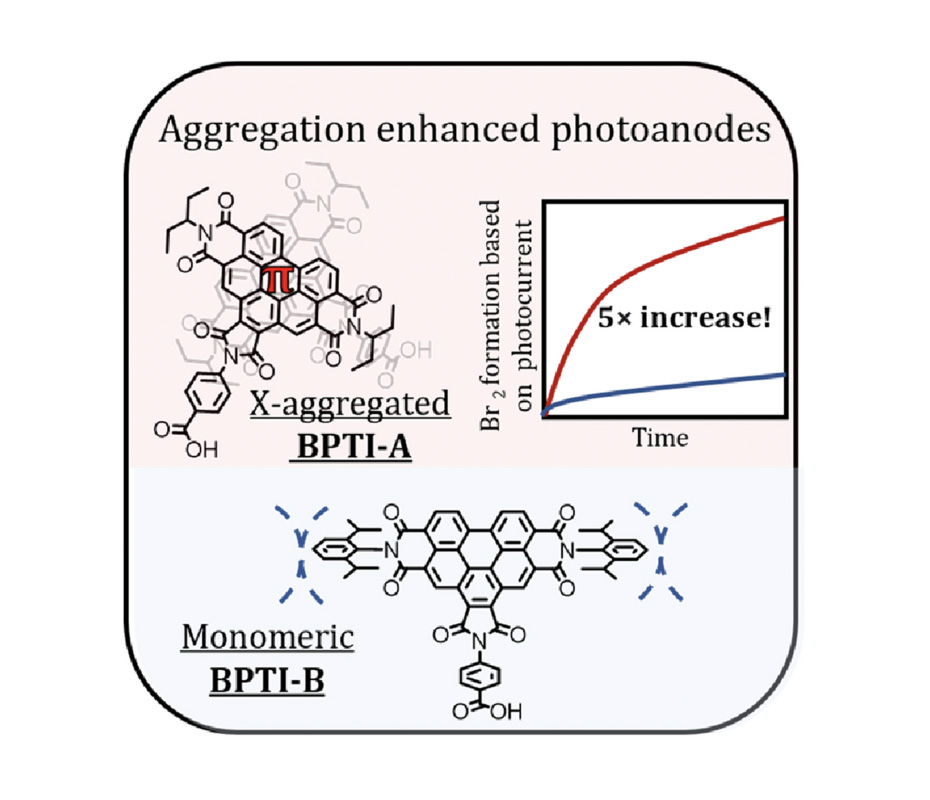
The impact of benzo[ghi]perylenetriimide (BPTI) dye aggregation on the performance of photoelectrochemical devices was explored, through imide-substitution with either alkyl (BPTI-A, 2-ethylpropyl) or bulky aryl (BPTI-B, 2,6-diisopropylphenyl) moieties, to, respectively, enable or suppress aggregation. While both dyes demonstrated similar monomeric optoelectronic properties in solution, adsorption onto mesoporous SnO2 revealed different behavior, with BPTI-A forming aggregates via π-stacking and BPTI-B demonstrating reduced aggregation in the solid state. BPTIphotoanodes were tested in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) before application to dye-sensitized photoelectrochemical cells (DSPECs) for Br2 production (a strong oxidant) coupled to H2 generation (a solar fuel). BPTI-A demonstrated a twofold higher dye loading of the SnO2 surface than BPTI-B, resulting in a fivefold enhancement to both photocurrent and Br2 production. The enhanced output of the photoelectrochemical systems (with respect to dye loading) was attributed to both J– and H-aggregation phenomena in BPTI-A photoanodes that lead to improved light harvesting. Our investigation provides a strategy to exploit self-assembly via aggregation to improve molecular light-harvesting and charge separation properties that can be directly applied to dye-sensitized photoelectrochemical devices.
Graphical Abstract
Increased Solar-Driven Chemical Transformations through Surface-Induced Benzoperylene Aggregation in Dye-Sensitized Photoanodes. Benzo[ghi]perylenetriimide (BPTI) dyes are investigated to reveal the effect of aggregation by π-stacking on photovoltaic parameters in dye-sensitized devices. Photoanodes with aggregating BPTIs show both J- and H- aggregation phenomena leading to enlarged visible light absorbance and increased electron injection. The use of aggregating BPTI outperforms a non-aggregation BPTI with fivefold in terms of photocurrent and product generation.